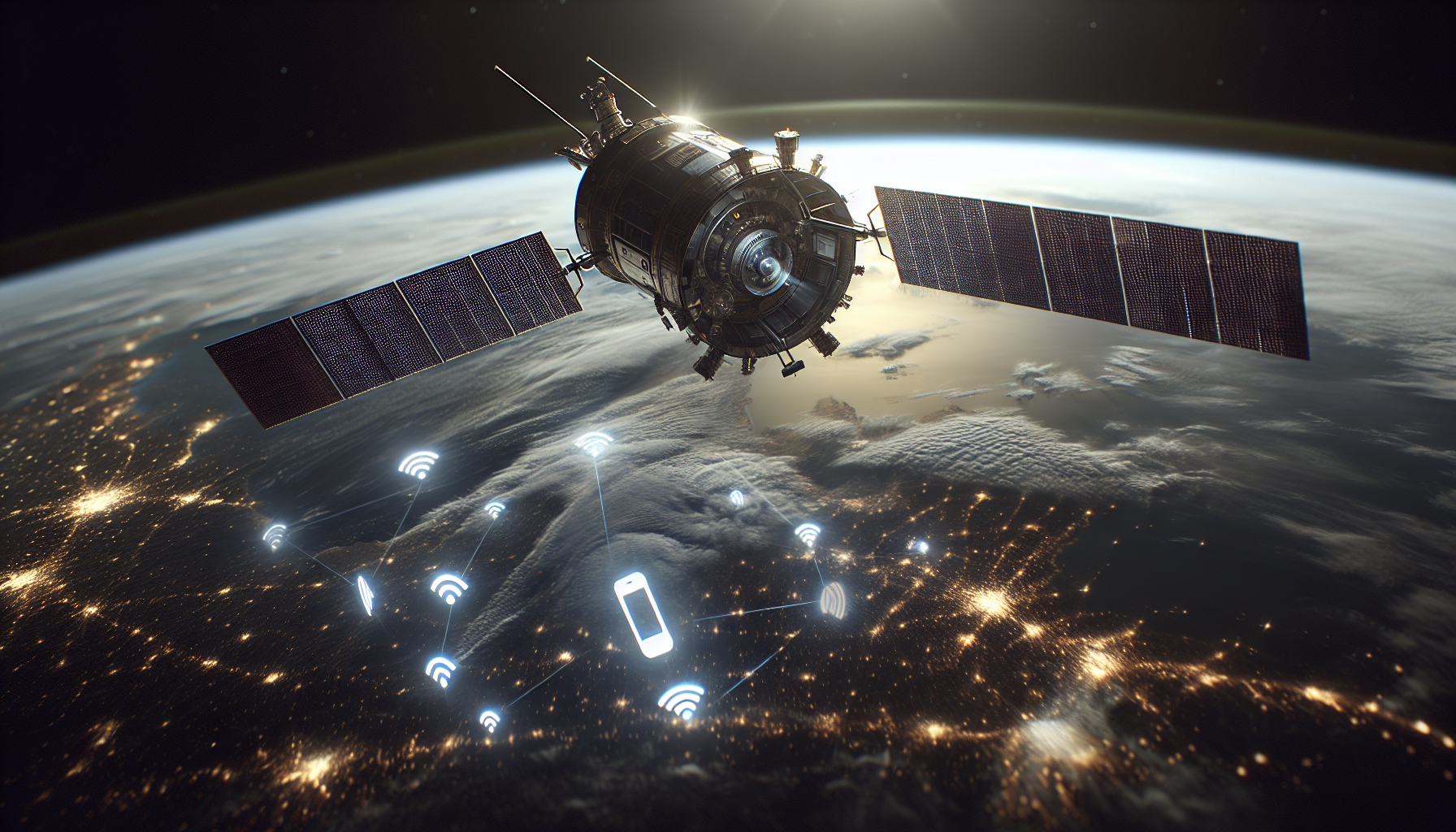
Starlink has rapidly emerged as a captivating venture in satellite technology, and its new direct-to-phone service is a remarkable step forward. This innovative move aims to elevate global mobile connectivity to unprecedented heights. As the demand for universal communication access continues to escalate, particularly in remote and underserved areas, Starlink’s technology promises to meet these pressing needs.
Utilizing a constellation of satellites designed to connect directly with everyday mobile phones through standard LTE/4G protocols, this groundbreaking service requires no special apps or hardware modifications. The recent launch of 20 new satellites, marking the completion of the first orbital shell, represents a significant milestone in this journey. Users can expect the service to begin with text messaging capabilities by the end of 2024, evolving to include voice and data services by 2025.
Revolutionizing Mobile Communication
The concept of direct-to-phone technology may sound revolutionary, and it certainly lives up to that description. The ability for ordinary smartphones to directly connect with satellites opens up a realm of possibilities. This technology employs onboard LTE modems within each satellite, which integrate seamlessly with existing cell networks. The implications for communication are profound — envision it as a lifeline when traditional infrastructures fall short.
In this rapidly evolving landscape, SpaceX’s vision of democratizing connectivity becomes evident. The deployment of these satellites isn’t merely about achieving technical milestones, but about effecting meaningful changes in global communication. The timeline of these advancements is nothing short of exciting. Text services will launch by late 2024, followed by the gradual rollout of voice and data services by 2025, resulting in reduced dependence on traditional cell towers.
Connecting Remote Users
The most significant impact of Starlink’s direct-to-phone satellites will likely be felt in rural and remote locations. In areas where constructing traditional network infrastructure is impractical or impossible, satellite communication presents a viable alternative. Picture farmers in expansive fields, hikers in remote valleys, or explorers venturing into uncharted territories — all equipped with reliable communication tools. This technology is poised to eliminate dead zones, ensuring no one is left disconnected, regardless of their geographic location.
The potential for connectivity “anywhere on Earth” not only serves as a convenience for travelers but also as a vital link for individuals and businesses operating in isolated communities. Starlink’s direct-to-phone service could empower local economies by facilitating communication that was once unattainable, enhancing emergency response capabilities, and creating continuous lines of contact.
Navigating Challenges Ahead
Despite these remarkable advancements, the road ahead is not without hurdles. Early adopters have expressed concerns regarding connectivity reliability, particularly given the initial bandwidth limitation of around 10 Mb. While this is adequate for standard communication needs, it may fall short for high-speed data requirements. This limitation positions the service more as a complement rather than a substitute for traditional networks.
Elon Musk has openly acknowledged that, while Starlink represents a significant advantage for remote connectivity, it does not directly challenge terrestrial cellular networks. This transparency is essential in aligning user expectations, particularly in regions where high-speed connectivity is the norm.
Reliability remains a crucial concern, especially as technology grows. Users in rural areas will be particularly observant of how these satellites perform under real-world conditions, balancing load and ensuring service quality. These practicalities will ultimately determine the service’s long-term sustainability and acceptance.
Increasing Competition in Satellite Communication
The competition for achieving reliable satellite-based mobile communication is intensifying, with new players entering the arena. Companies like Lynk and AST SpaceMobile have made notable advances in this field. Lynk, for example, has successfully demonstrated satellite text services in Palau, showcasing a tangible application of their technology.
Each competitor brings distinct offerings to the table, and the differences between them could significantly influence market dynamics. AST SpaceMobile’s emphasis on wideband broadband capabilities versus Lynk’s immediate text solutions indicate differing service priorities, addressing various consumer needs and geographical challenges. These developments introduce exciting challenges and opportunities as the satellite telecommunications landscape evolves.
Envisioning Future Connectivity
The horizon of satellite communications is rich with potential. As technologies mature, increasingly sophisticated use cases are likely to surface. Beyond bridging disconnected regions, there’s the possibility of integrating IoT devices, transforming industries ranging from agriculture to logistics by facilitating reliable, widespread connectivity that truly spans the globe.
As satellite networks expand, they could enhance, if not fully transform, existing communication infrastructures. These shifts highlight a broader trend toward ubiquitous connectivity, where distances and logistical barriers become increasingly negligible. Each new satellite launched into orbit brings us closer to a world where every corner of our planet is merely a phone call away.
Starlink’s direct-to-phone satellites symbolize an era where groundbreaking innovation meets real-world challenges, crafting solutions that push the boundaries of what’s achievable in global communication.